

short int may also be specified as just short.printf and scanf replace %d or %i with %hd or%hi to indicate the use of a short int.On many machines short ints use the same number of bits as regular ints. ( The C standard only specifies that a short int cannot use more bits than a regular int.A short int may use fewer bits than a regular int, thereby saving storage space.C99 introduces the long long int, typically having twice as many bits as a long int and printed/scanned using %lld or %lli format specifiers.long int may also be specified as just long.printf and scanf replace %d or %i with %ld or %li to indicate the use of a long int.( The C standard only specifies that a long cannot use a fewer number of bits than a regular int ).A long int typically uses twice as many bits as a regular int, allowing it to hold much larger numbers.Format specifiers for ints are either %d or %i, for either printf or scanf.The int data type is always the "best" size for the particular computer it is running on, typically 32 bits.The most basic and commonly used integral type is "int".Specific details of the integer types available on a particular implementation, along with the number of bits allocated to each one and their minimum and maximum allowable values can be found in the file limits.h.Signed integers use half of the possible bit patterns to represent negative numbers, one pattern to represent zero, and half minus 1 to represent positive values.Unsigned integers use one bit pattern ( all 0s ) to represent zero and all others to represent positive values.Signed and unsigned integers with the same number of total bits have the same number of different possible values.A signed integral type having all bits 1 is equal to -1, regardless of how many bits are in the number.So for example, a 4-bit signed integer could range from -8 to +7, and an 8-bit signed integer could range from -128 to +127.The most positive value would be the first bit a 0 and all other bits 1s, yielding 2^(N-1) - 1.The most negative value would be the first bit a 1 and all other bits 0s, yielding negative 2^(N-1).( The real interpretation in the computer is more complicated, but if you think of it this way you will get the right answers.For signed integral types, the leftmost bit can be thought of as representing a negative 2^(N-1).So for example, a 4-bit unsigned integer could range from 0 to 15, and an 8-bit unsigned integer could range from 0 to 255.The range of possible values for an unsigned integer of N bits is from 0 to 2^N - 1.For unsigned integral types, the leftmost bit, known as the most significant bit, represents 2^(N-1), where N is the total number of bits in the data item.In general the nth bit from the right represents 2^(n-1).The next bit represents the number of 8s.
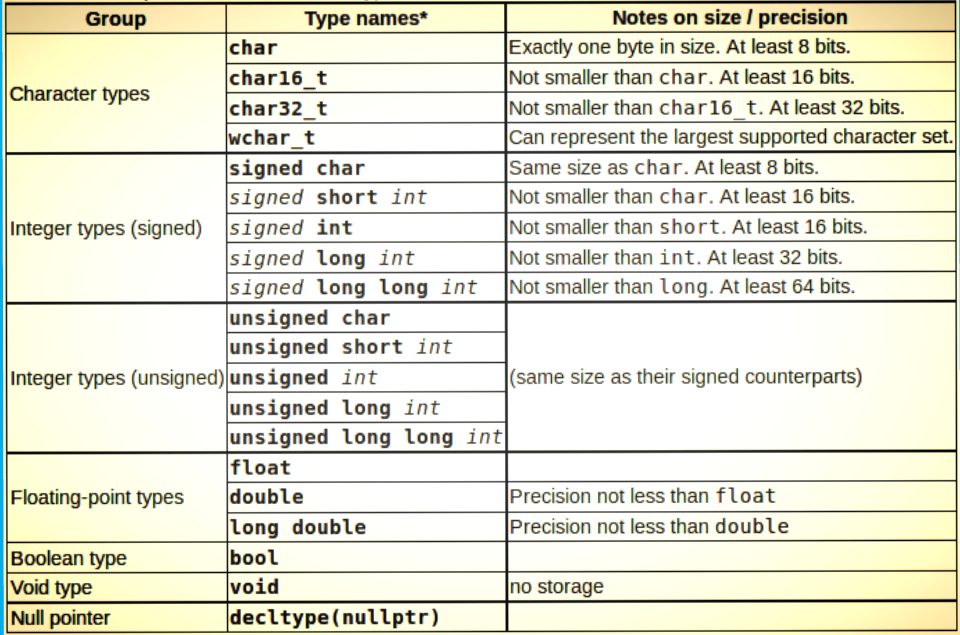
The next bit represents the number of 4s.The next bit represents the number of 2s.The right-most bit, known as the least significant bit, represents the number of 1s.The bits of integral types are interpreted as simple powers of two:.Integral data types include all whole numbers, that is numbers not having any fractional component.Data may be converted from one type to another, ( possibly with loss of precision ), and new types may be user defined.Modern C adds a few special types to this list. Basic C recognizes four basic categories of data types: Integral, Floating Point, Character, and Character String.The "type" of a particular variable or constant determines how many bits are used used for that paticular data item, and how the bits are to be interpreted.Physically these zeros and ones may be implemented using wires with two different voltages, magnetic particles with two different alignments, spots on an optical disk having two different optical properties, or by other means.These binary digits are referred to as "bits".Ultimately all data stored on a computer, both variables and constants, is stored as a sequence of binary digits, e.g.Constants are values that are hard-coded into a program, and which do not chnage value.Variables are named storage locations where data is stored, which may be changed as a program runs.Summary Sheet Fundamentals of Data Storage


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
